Overview
The Secure Development Policy (P24S) provides SMEs with clear, enforced standards for secure coding, review, and deployment, aligning with ISO 27001, GDPR, DORA, and NIS2. It centralizes oversight with the General Manager, ensuring all internally developed or third-party software complies with regulatory and contractual obligations, from secure coding to vendor management and audit readiness.
Enforced Secure Coding
Mandates secure development practices for all code, minimizing vulnerabilities and data risks.
SME-Friendly Roles
Designed for SMEs, assigning development security oversight to the General Manager, not requiring a dedicated IT team.
Audit-Ready Documentation
Requires retention of checklists and approvals for easy ISO 27001 audit and customer assurance.
Vendor & Third-Party Controls
Enforces security clauses in all third-party development contracts and tracks compliance.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
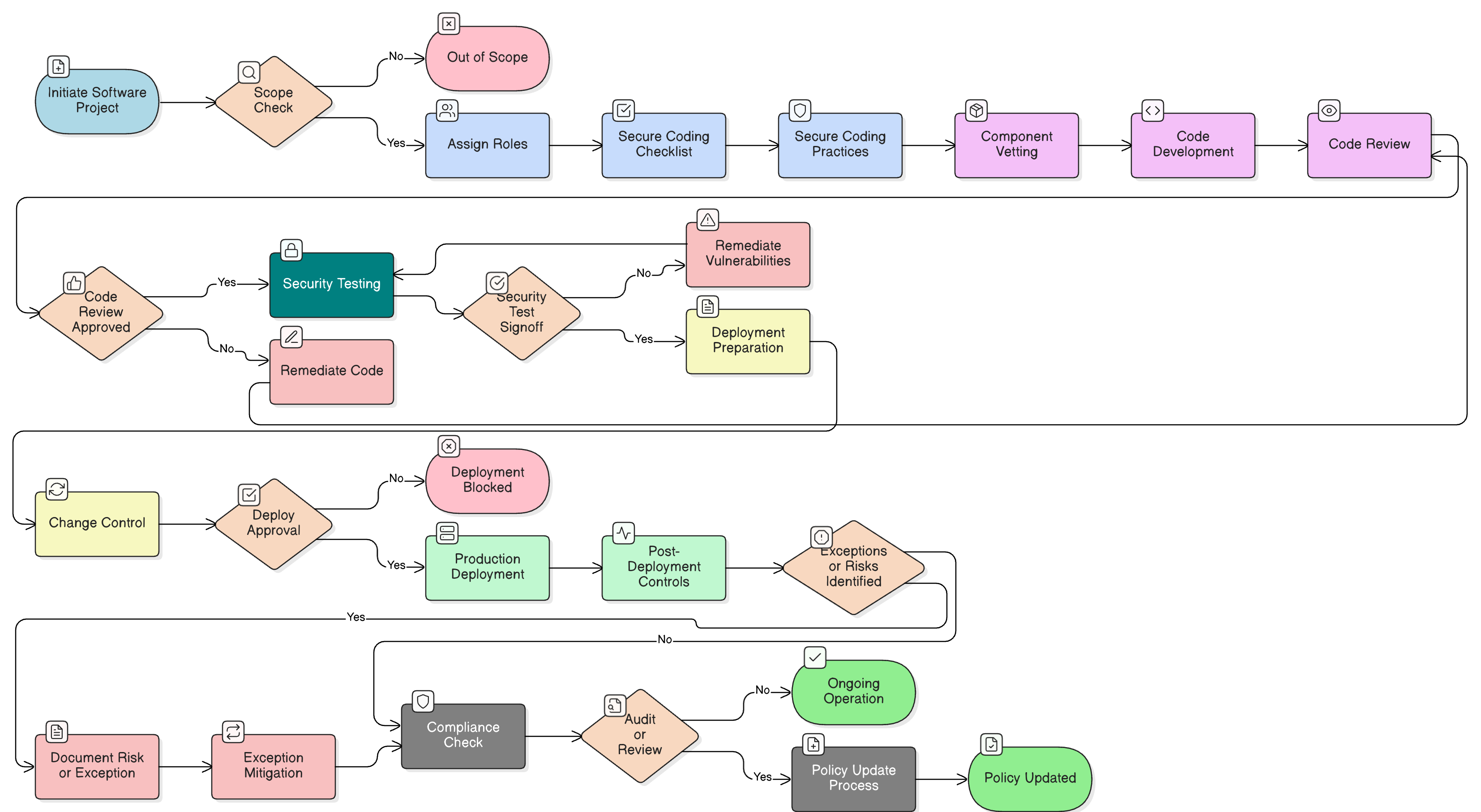
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Secure Coding and Review Requirements
Application Security Testing Procedures
Third-Party and Open-Source Component Controls
Deployment and Change Control Procedures
Risk Treatment and Exception Handling
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
| Framework | Covered Clauses / Controls |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | |
| ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | |
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5 | |
| EU GDPR |
Article 25
|
| EU NIS2 | |
| EU DORA | |
| COBIT 2019 |
Related Policies
Governance Roles And Responsibilities Policy-SME
Establishes accountability for assigning and verifying development security controls across projects and vendors.
Access Control Policy-SME
Provides baseline rules for limiting access to development environments and code repositories, including separation of duties.
Information Security Awareness And Training Policy-SME
Ensures internal developers and contractors understand secure coding practices and related security responsibilities.
Data Protection And Privacy Policy-SME
Clarifies how personal data must be handled during development, testing, and logging processes to stay GDPR compliant.
Incident Response Policy-SME
Defines how development-related security incidents must be reported, assessed, and remediated, including code-related exposures.
About Clarysec Policies - Secure Development Policy - SME
Generic security policies are often built for large corporations, leaving small businesses struggling to apply complex rules and undefined roles. This policy is different. Our SME policies are designed from the ground up for practical implementation in organizations without dedicated security teams. We assign responsibilities to the roles you actually have, like the General Manager and your IT Provider, not an army of specialists you don't. Every requirement is broken down into a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.2.1, 5.2.2). This turns the policy into a clear, step-by-step checklist, making it easy to implement, audit, and customize without rewriting entire sections.
Structured Deployment Controls
Requires version tracking, backup, and rollback steps for every production release, minimizing disruption from failed deployments.
Clear Separation of Environments
Mandates strict controls to keep development, testing, and production environments isolated for better security and integrity.
Proactive Risk Exception Handling
Formalizes risk assessment and GM approval for any deviation, with clear documentation and review cycles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
