Overview
This policy details required security measures for IoT and OT systems, including lifecycle controls, network isolation, monitoring, secure procurement, and compliance alignment.
End-to-End IoT/OT Protection
Mandatory security controls across the lifecycle of connected industrial and IoT systems safeguard critical operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Aligns with standards like ISO/IEC 27001, NIST, GDPR, NIS2, and DORA for robust compliance and sector readiness.
Secure Procurement & Monitoring
Requires vetted devices, secure deployment, continuous monitoring, and strong vendor contract clauses.
Incident-Ready Response
Integrates with incident response plans for swift escalation and cross-team coordination in OT/IoT breaches.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
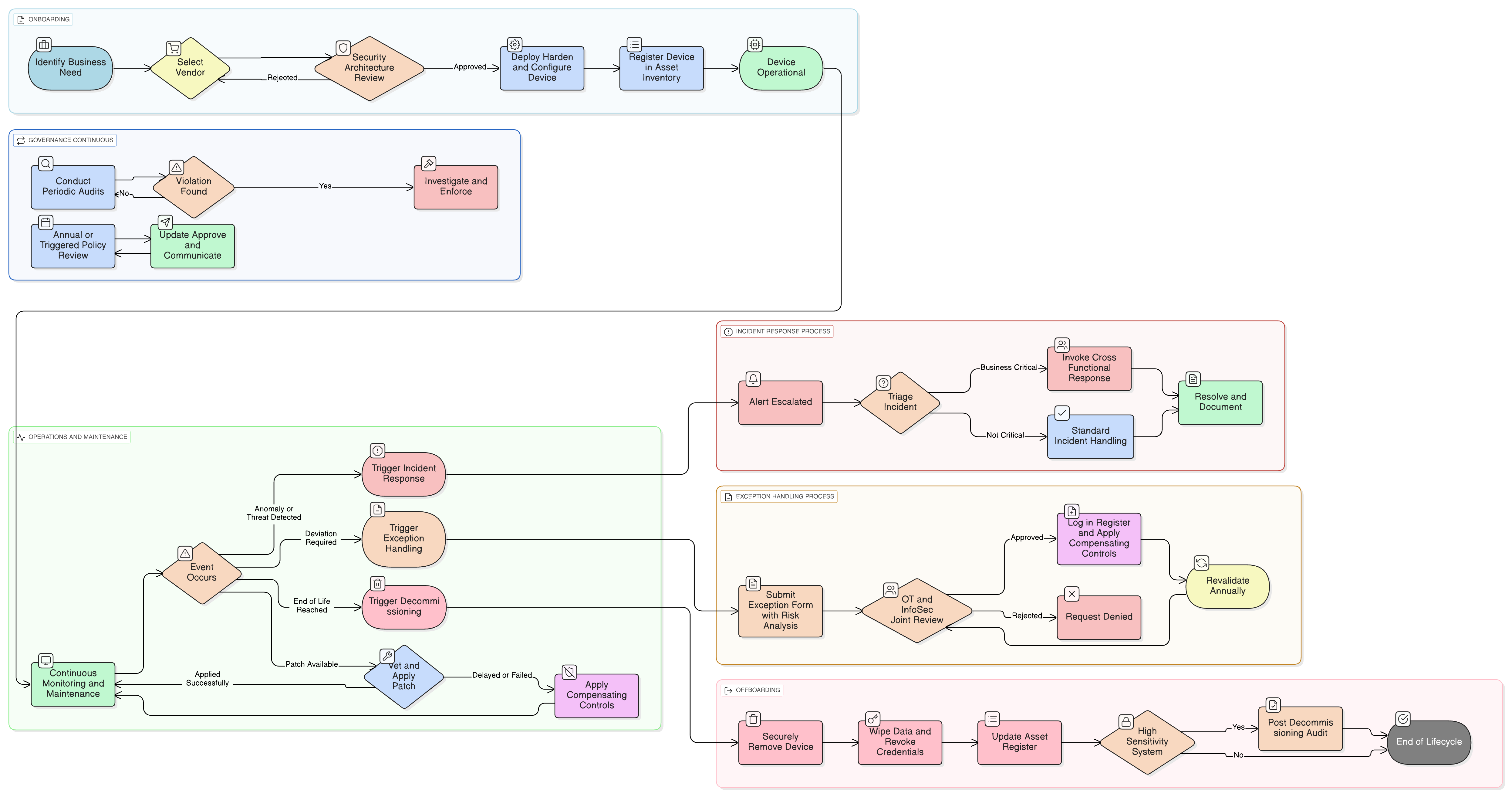
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Lifecycle Security Controls (Design to Decommissioning)
Network Segmentation and Device Hardening
Monitoring, Logging, and Threat Detection
Incident Escalation Procedures
Vendor and Procurement Security Requirements
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
Related Policies
Information Security Policy
Establishes foundational security principles that extend to IoT and OT system security.
Endpoint Protection And Malware Policy
Applies to connected controllers, smart gateways, and edge systems in production.
Audit Compliance Monitoring Policy
Provides assurance mechanisms to validate ongoing compliance with this policy.
Acceptable Use Policy
Defines restrictions on personal and unauthorized device use, including in operational environments.
Risk Management Policy
Guides the assessment, acceptance, and mitigation of risks related to embedded and control systems.
Asset Management Policy
Ensures all IoT and OT systems are formally inventoried and assigned responsible owners.
Logging And Monitoring Policy
Extends to log capture and review procedures for OT environments.
Incident Response Policy
Directly governs how IoT/OT breaches, anomalies, or system failures must be escalated and managed.
About Clarysec Policies - IoT-OT Security Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Clear Role Assignments
Responsibility mapped to actual enterprise roles (CISO, OT, IT, Vendor) for accountable execution and oversight of every requirement.
Lifecycle Traceability
Numbered clauses and structured requirements enable step-by-step tracking from deployment to decommissioning and audit.
Exception & Risk Controls
Built-in exception process with formal risk analysis, enabling safe overrides for legacy or constrained devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
