Overview
The Logging and Monitoring Policy defines comprehensive requirements for capturing, protecting, and analyzing logs from all critical IT infrastructure, supporting incident detection, compliance, and audit readiness.
Comprehensive Log Coverage
Mandates logging for all critical systems, applications, and events, supporting investigation, audit, and regulatory needs.
Centralized SIEM Integration
Requires aggregation and correlation of logs in a protected SIEM, enabling rapid detection and escalation of security anomalies.
Regulatory Compliance Ready
Directly aligned with ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, NIS2, DORA, and COBIT 2019 requirements for monitoring and audit trails.
Strict Retention and Protection
Defines secure retention, backup, and controls to prevent log tampering and ensure data integrity.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
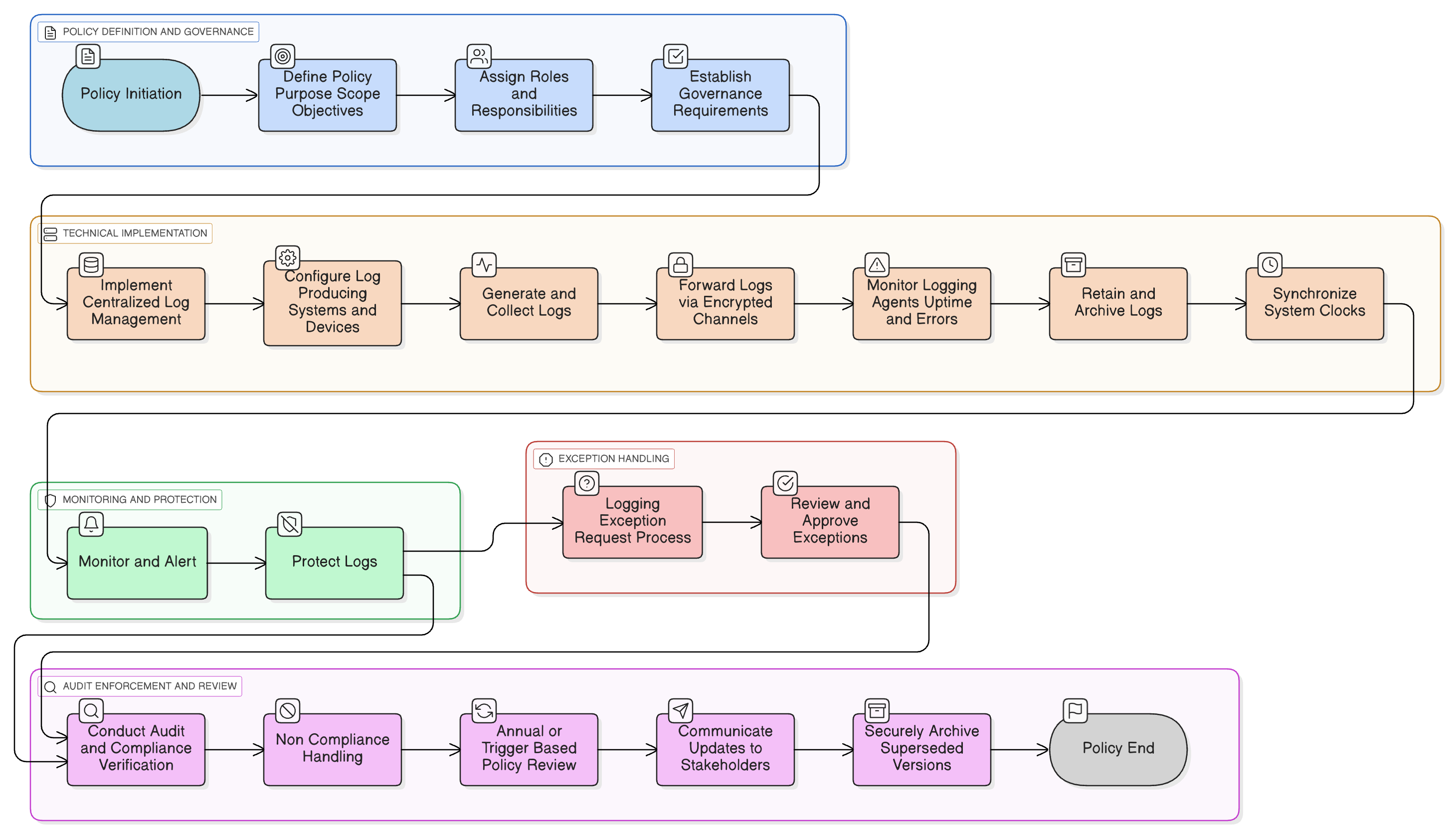
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Event Types and Logging Requirements
Roles and Responsibilities
Centralized SIEM and Alerting
Log Retention and Protection
Exception Management Process
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
Related Policies
Information Security Policy
Establishes the foundational commitment to protect systems and data, under which logging and monitoring act as critical detective and response enablers.
Access Control Policy
Ensures that privileged access, user logins, and authorization events are captured in logs and monitored for abuse or anomalous behavior.
Change Management Policy
Mandates logging of system changes, patch deployments, and configuration updates that can introduce risk or unauthorized modifications.
Network Security Policy
Requires network-level logging (e.g., firewall logs, IDS/IPS alerts, VPN activity) and integration with SIEM for visibility into traffic anomalies and boundary defense.
Time Synchronization Policy
Enforces clock consistency across systems, which is essential for reliable logging and correlation of security events across multiple environments.
Incident Response Policy
Relies on log data and alerting mechanisms to identify, investigate, and respond to security incidents, while also preserving forensic artifacts for post-incident review.
About Clarysec Policies - Logging and Monitoring Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Defined Stakeholder Responsibilities
Assigns clear duties to CISO, SOC, IT admins, developers, and vendors with mapped escalation paths for anomalies and compliance gaps.
Exception Handling Workflow
Formal LER process enables safe logging exceptions, risk analysis, and mandatory periodic reviews to manage unavoidable gaps.
Time Synchronization Enforcement
Mandates NTP-clock sync across all systems for accurate log correlation, with alerting on failures to protect forensic integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
