Overview
This policy sets minimum, mandatory security requirements for all software applications used by the organization, specifying controls for authentication, encryption, access, and logging. It is streamlined for SME environments, placing overall responsibility with the General Manager and covering both internally developed and vendor-supplied applications to achieve compliance and reduce security risks.
Comprehensive Security Controls
Mandates baseline controls like authentication, encryption, and audit logging for all applications, protecting sensitive data.
SME-Adapted Simplicity
Tailored for small and medium businesses with simplified roles, centralized by the General Manager, not requiring dedicated IT teams.
Vendor & Cloud Compliance
Ensures third-party software and cloud services meet minimum security criteria and are contractually bound to requirements.
Privacy & Regulatory Alignment
Supports GDPR, NIS2, DORA, and ISO/IEC 27001 compliance for protection by design and by default.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
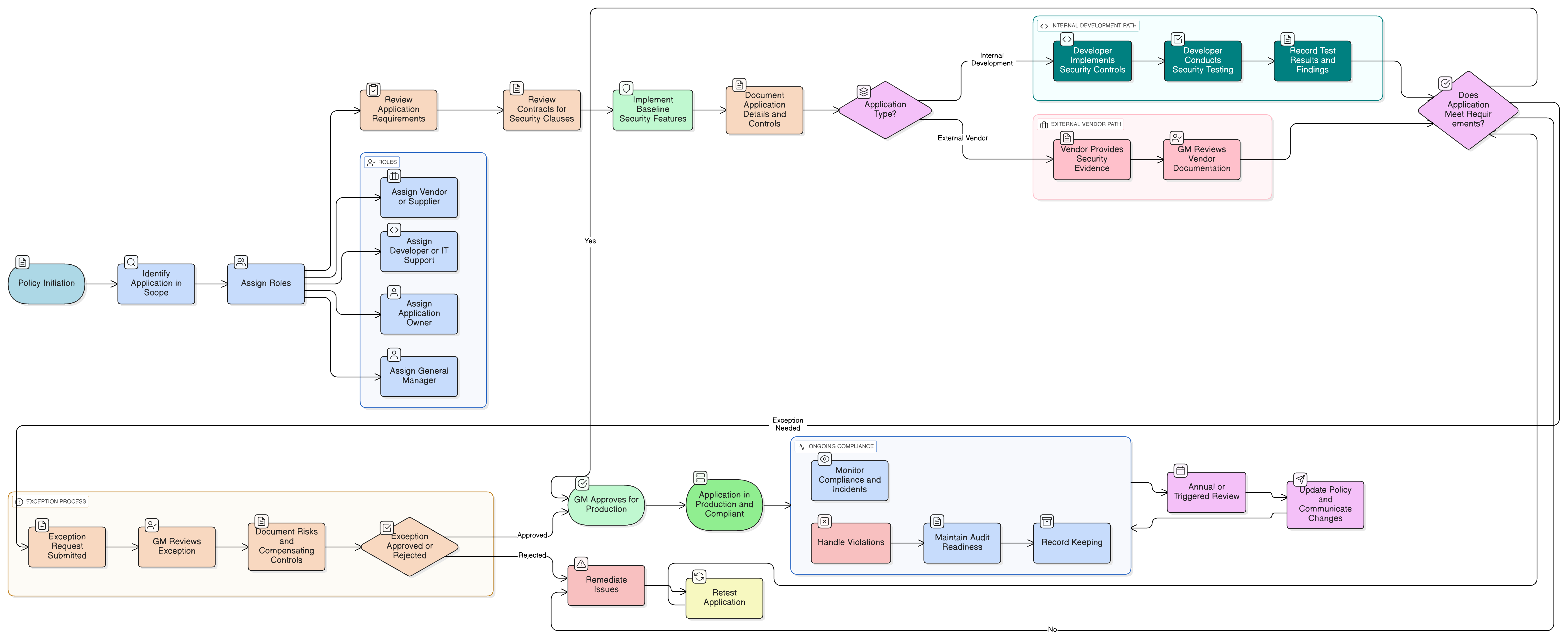
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Roles (General Manager, Developers, Vendors)
Mandatory Application Security Controls
Third-Party & Cloud Application Security
Testing and Validation Requirements
Data Privacy & Handling Procedures
Exception and Risk Treatment Process
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
| Framework | Covered Clauses / Controls |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | |
| ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | |
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5 | |
| EU GDPR |
Article 25
|
| EU NIS2 | |
| EU DORA | |
| COBIT 2019 |
Related Policies
Governance Roles And Responsibilities Policy-SME
Assigns responsibility for approving applications, enforcing policy, and managing vendors.
Access Control Policy-SME
Ensures application access aligns with minimum privilege and session control principles.
Information Security Awareness And Training Policy-SME
Ensures users and developers are trained in recognizing and reporting application-related threats.
Data Protection And Privacy Policy-SME
Provides data privacy safeguards that must be enforced by any application processing personal information.
Data Retention And Disposal Policy-SME
Governs how application-generated logs, backups, and sensitive data must be retained, archived, and destroyed securely.
Incident Response Policy-SME
Outlines steps for identifying, reporting, and containing application-related security events.
About Clarysec Policies - Application Security Requirements Policy - SME
Generic security policies are often built for large corporations, leaving small businesses struggling to apply complex rules and undefined roles. This policy is different. Our SME policies are designed from the ground up for practical implementation in organizations without dedicated security teams. We assign responsibilities to the roles you actually have, like the General Manager and your IT Provider, not an army of specialists you don't. Every requirement is broken down into a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.2.1, 5.2.2). This turns the policy into a clear, step-by-step checklist, making it easy to implement, audit, and customize without rewriting entire sections.
Audit-Ready Documentation
Maintains security test reports, exception records, and vendor confirmations for easy compliance checks and audits.
Enforced Exception Process
Waivers from security controls require formal GM approval, risk review, and documentation, no silent gaps.
Critical Third-Party Component Control
Open source and plugins are tracked, scanned, and reviewed annually. Unpatchable risks require prompt removal or replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
