Overview
This policy governs the security, risk, and compliance requirements for all third-party and supplier relationships, detailing due diligence, contractual safeguards, ongoing monitoring, and offboarding procedures for third parties handling organizational data or services.
Comprehensive Supplier Oversight
Mandates rigorous security controls, risk tiering, and audits for all third-party providers throughout their service lifecycle.
Contractual Security Safeguards
Ensures supplier contracts include breach notification, data handling, right-to-audit, and enforceable compliance clauses.
Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Requires regular performance reviews, certification audits, and incident escalation to maintain third-party accountability.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
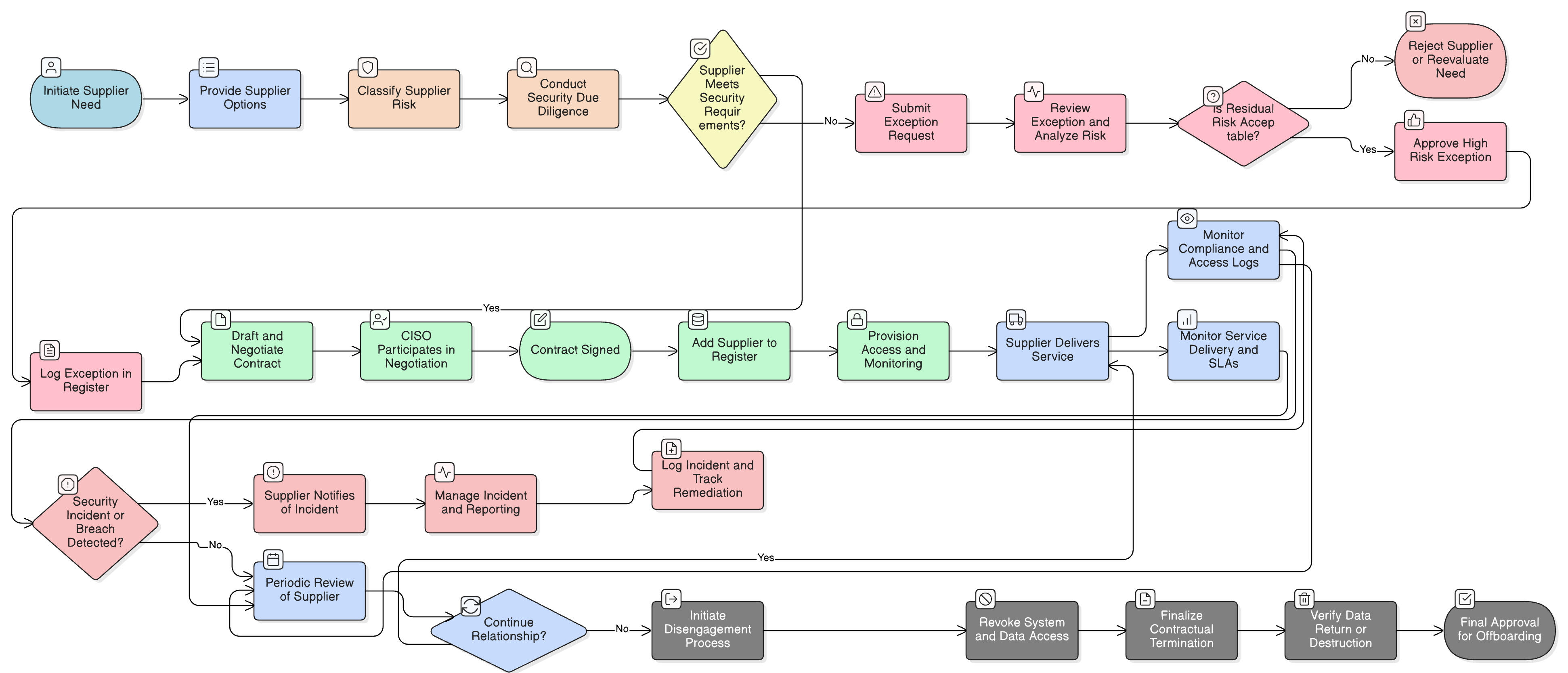
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Supplier Due Diligence Requirements
Third-Party Risk Classification & Tiering Model
Contractual Security Clauses
Continuous Performance and Compliance Reviews
Termination and Offboarding Protocols
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
Related Policies
Information Security Policy
Establishes the overarching commitment to secure all organizational operations, including reliance on third-party suppliers and external service providers.
Risk Management Policy
Guides the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks associated with third-party relationships, including inherited or systemic risks from supplier ecosystems.
Data Protection And Privacy Policy
Applies to all suppliers that handle personal data, requiring appropriate contractual terms, transfer safeguards, and privacy-by-design principles.
Access Control Policy
Controls how third-party personnel gain access to organizational systems, enforcing role-based permissions, session controls, and revocation procedures.
Logging And Monitoring Policy
Requires that supplier access to systems be monitored, logged, and reviewed, particularly in environments where privileged or data-centric activities occur.
Incident Response Policy
Defines escalation procedures and breach reporting requirements for supplier-originated security events or joint investigations involving third-party systems.
About Clarysec Policies - Third-Party and Supplier Security Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Exception Management Built-In
Features a formal process for supplier security exceptions, requiring rationale, risk analysis, and time-bound controls.
Lifecycle Process Integration
Integrates security into procurement, onboarding, service monitoring, and offboarding for every supplier relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
