Overview
This Secure Development Policy sets mandatory requirements for embedding security controls at every stage of software development, ensuring all code, internal, outsourced, or third-party, undergoes rigorous security validation and aligns with leading standards such as ISO/IEC 27001:2022, NIST SP 800-53, GDPR, and more.
End-to-End Security
Enforces security controls throughout every phase of development to proactively reduce risk.
Mandatory Secure Coding
Requires use of OWASP, SANS, and language-specific coding standards, peer reviews, and automated testing.
Role-Based Oversight
Defines clear responsibilities for CISO, DevSecOps, developers, QA, and third-party suppliers.
Compliance and Audit
Aligns with ISO/IEC 27001:2022, NIST SP 800-53, GDPR, NIS2, and DORA for strong regulatory coverage.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
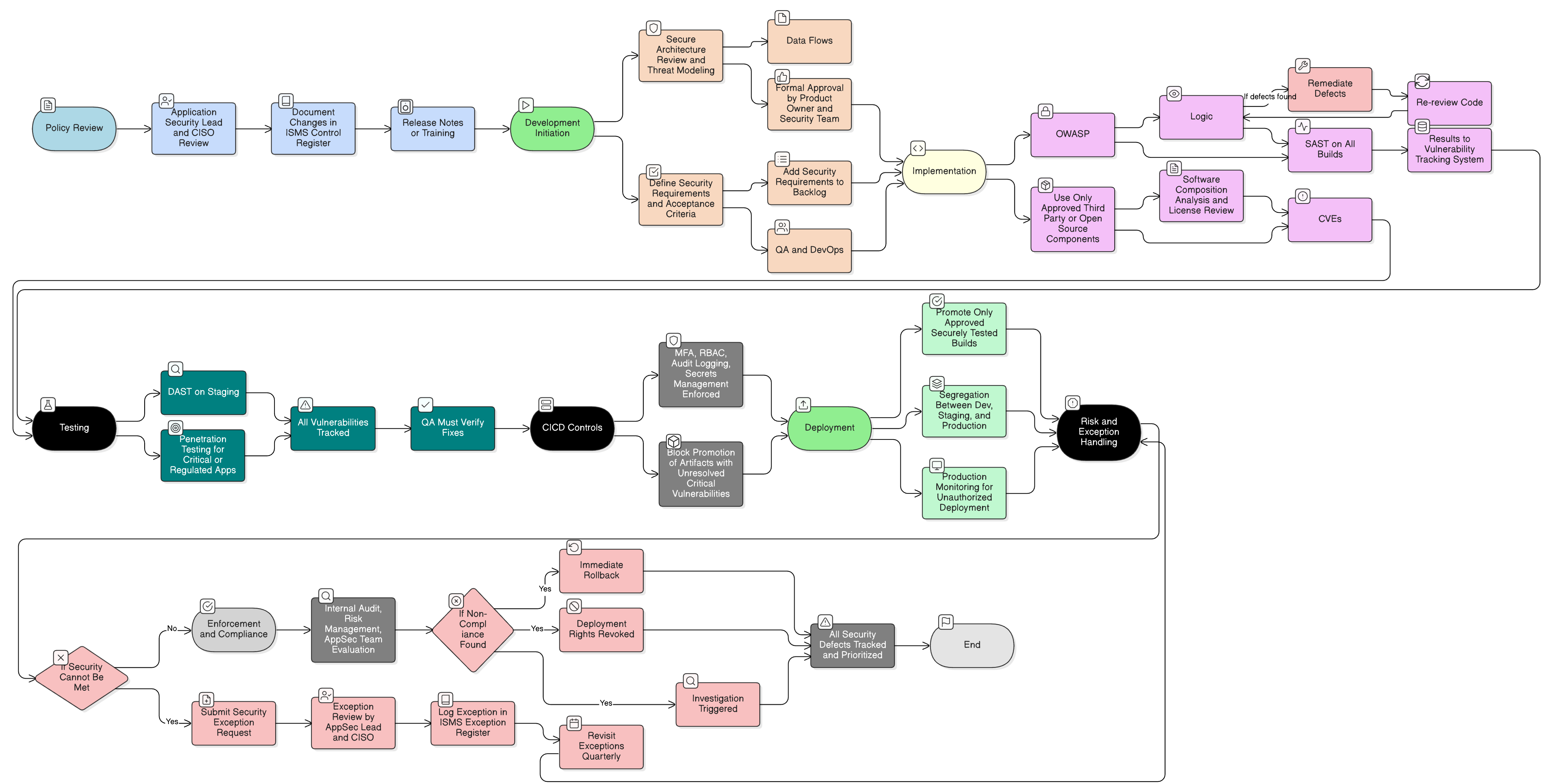
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Secure SDLC Governance Requirements
Role-Specific Responsibilities
Code Review and Security Testing Requirements
Exception and Risk Treatment Process
Alignment with Standards and Regulations
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
Related Policies
Information Security Policy
Sets the strategic mandate for embedding security across all information systems, of which secure development is a foundational operational control.
Access Control Policy
Defines the control measures for restricting access to development environments, repositories, build tools, and CI/CD pipelines.
Change Management Policy
Ensures that code changes, releases, and deployments are subject to proper approval, rollback planning, and post-deployment verification.
Asset Management Policy
Supports the inventorying of development environments, source repositories, and build systems as managed assets subject to classification and protection.
Logging And Monitoring Policy
Applies to development pipelines, ensuring that build processes, code promotions, and deployment events are logged, monitored, and analyzed for security anomalies.
Incident Response Policy
Provides the framework for analyzing and responding to security flaws discovered post-deployment or during application security testing.
About Clarysec Policies - Secure Development Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Rigorous Third-Party Code Governance
Requires formal validation, vulnerability scanning, and supply chain security reviews for all outsourced and open-source components.
Controlled Dev/Test Environments
Mandates segregation, scrubbed datasets, and blocked internet access for non-production systems to prevent data leakage.
Exception Management Workflow
Provides a structured process for risk-based exception requests, approval, and periodic review for traceable deviation handling.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
