Overview
The Backup and Restore Policy mandates organizational requirements for backup frequency, retention, security, restoration, and compliance, protecting against data loss and ensuring recovery in alignment with leading standards and business continuity objectives.
Ensures Data Protection
Defines requirements to safeguard against data loss, corruption, and cyberattacks through resilient backup strategies.
Regulatory Compliance
Aligns with ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR, DORA, and NIS2 for compliant data retention, backup, and restoration.
Operational Resilience
Integrates with business continuity plans to support rapid, reliable recovery in case of incidents.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
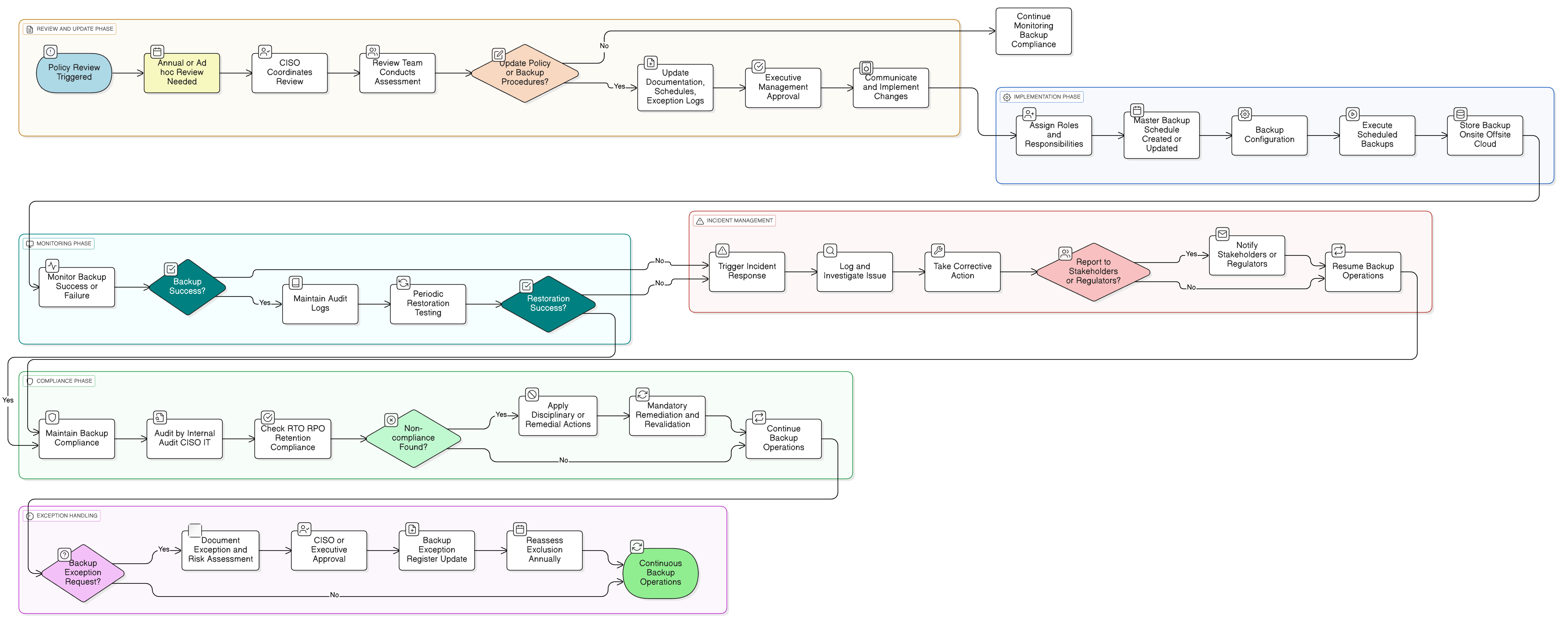
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Backup and Restoration Requirements
Third-Party and Cloud Backup Controls
Governance and Testing
Retention and Secure Disposal Procedures
Exception Management and Risk Treatment
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
| Framework | Covered Clauses / Controls |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | |
| ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | |
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5 | |
| EU GDPR |
Article 32Recital 49
|
| EU NIS2 | |
| EU DORA | |
| COBIT 2019 |
Related Policies
Risk Management Policy
Identifies risk-based prioritization of backup protection for systems and services.
Asset Management Policy
Ensures that backup-eligible systems are inventoried and tied to lifecycle tracking and classification.
Data Classification And Labeling Policy
Guides which data categories require backup, including labeling metadata for prioritization.
Data Retention And Disposal Policy
Coordinates backup retention with regulatory retention limits and proper disposal of expired media.
Data Masking And Pseudonymization Policy
Supports data minimization during backup of sensitive datasets.
Incident Response Policy
Activated during backup failures, restoration issues, or compromise of backup data repositories.
About Clarysec Policies - Backup and Restore Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Tested Restoration Procedures
Mandates restoration drills and integrity checks, ensuring backups work in practice and systems are truly recoverable.
Immutable and Auditable Backups
Backups are protected with strict immutability, versioning, and complete audit trails to prevent tampering or unauthorized changes.
Granular Role Accountability
Clear assignment of backup duties to Executive Management, CISO, IT, and business owners removes operational ambiguity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
