Overview
This SME-adapted Vulnerability and Patch Management Policy sets forth clear requirements for identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities in all organizational systems, ensuring rapid response, compliance with key frameworks, and manageable processes suitable for small and mid-sized enterprises.
Protect Against Vulnerabilities
Defines practices for rapid identification and mitigation of technical vulnerabilities across all systems.
SME-Friendly Responsibilities
Assigns practical accountability to General Managers and IT providers, reflecting simplified SME roles.
Audit and Compliance Readiness
Mandates thorough patch tracking and documentation for audits and regulatory reviews.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
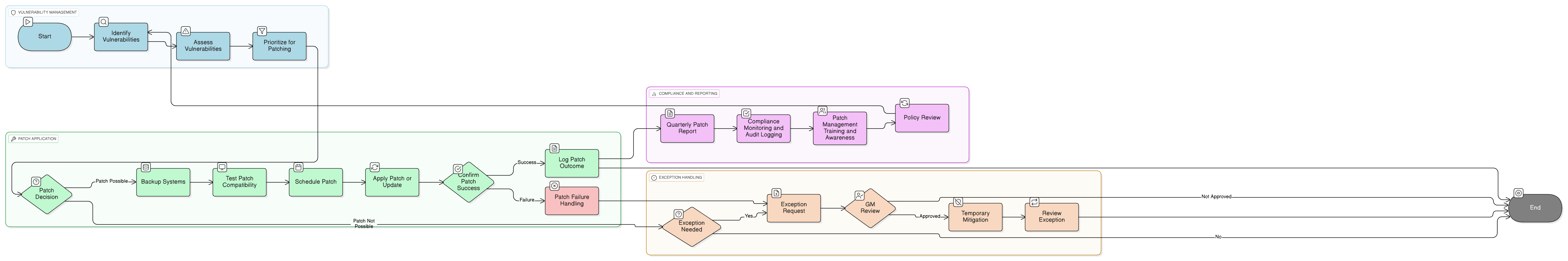
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Roles and Responsibilities
Patch Schedule and Timeframes
Vulnerability Monitoring Sources
Exception Handling Process
Audit and Compliance Requirements
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
Related Policies
Asset Management Policy-SME
Identifies system ownership and classification, ensuring that all assets requiring patching are accounted for and inventoried.
Data Retention And Disposal Policy-SME
Ensures that systems scheduled for decommissioning are securely updated or wiped, reducing vulnerability exposure.
Data Protection And Privacy Policy-SME
Prioritizes vulnerability remediation for systems processing personal data to comply with privacy laws.
Logging And Monitoring Policy-SME
Supports detection of unpatched systems or suspicious behaviors that may signal a vulnerability being exploited.
Incident Response Policy-SME
Defines procedures for responding to vulnerabilities that result in security incidents, including escalation and reporting steps.
About Clarysec Policies - Vulnerability and Patch Management Policy - SME
Generic security policies are often built for large corporations, leaving small businesses struggling to apply complex rules and undefined roles. This policy is different. Our SME policies are designed from the ground up for practical implementation in organizations without dedicated security teams. We assign responsibilities to the roles you actually have, like the General Manager and your IT Provider, not an army of specialists you don't. Every requirement is broken down into a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.2.1, 5.2.2). This turns the policy into a clear, step-by-step checklist, making it easy to implement, audit, and customize without rewriting entire sections.
Fast-Tracked Patch Schedules
Critical patches are enforced within 3 days and all others within 30 days, minimizing SME risk and downtime.
SME-Compatible Exception Handling
Documented, risk-based patch exceptions with practical mitigation and 90-day reviews for accessible governance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
