Overview
This policy sets mandatory security requirements for all organizational applications, ensuring secure design, development, and operation in alignment with global standards.
Comprehensive Coverage
Applies to all in-house, third-party, and SaaS applications across all environments and teams.
Lifecycle Security Integration
Enforces controls, testing, and validation from planning to post-deployment to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Governance and Compliance
Aligns with global standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, NIS2, and DORA for assurance and audit readiness.
Clear Roles and Accountability
Defines security responsibilities for development, operations, product, and third-party stakeholders.
Read Full Overview
Policy Diagram
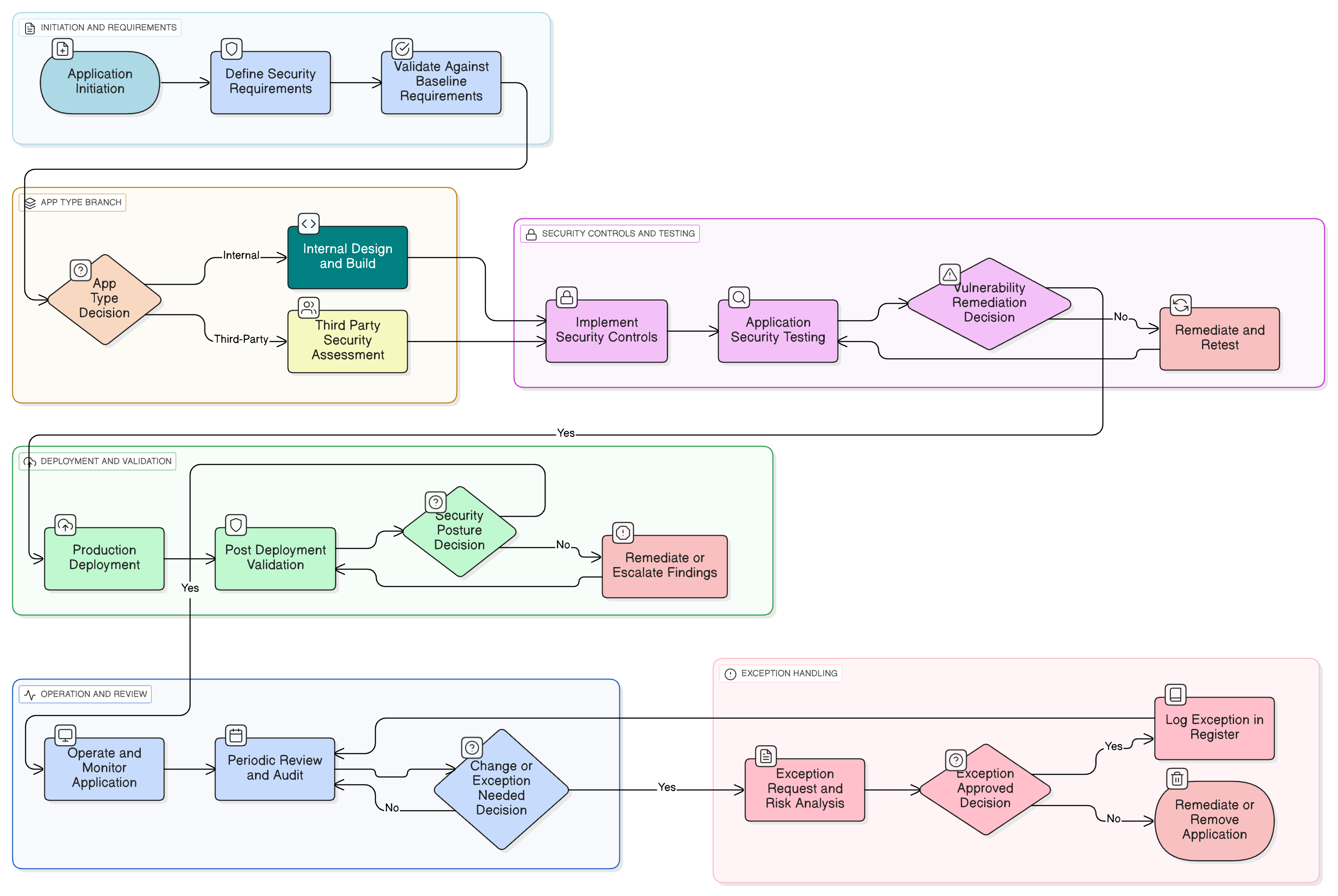
Click diagram to view full size
What's Inside
Scope and Rules of Engagement
Mandatory Security Functions and Controls
Secure API and Integration Requirements
Authentication and Access Control Alignment
Code Security Testing Methodology
Exception and Risk Treatment Process
Framework Compliance
🛡️ Supported Standards & Frameworks
This product is aligned with the following compliance frameworks, with detailed clause and control mappings.
| Framework | Covered Clauses / Controls |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | |
| ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | |
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5 | |
| EU GDPR |
2532
|
| EU NIS2 | |
| EU DORA | |
| COBIT 2019 | |
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | |
| ISO/IEC 27002:2022 | |
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5 | |
| EU GDPR |
2532
|
| EU NIS2 | |
| EU DORA | |
| COBIT 2019 |
Related Policies
Information Security Policy
Establishes the foundation for protecting systems and data, under which application-level controls are required to prevent unauthorized access, data leakage, and exploitation.
Access Control Policy
Defines the identity and session management standards that must be enforced by all applications, including strong authentication, least privilege, and access review requirements.
Change Management Policy
Regulates the promotion of application code and configurations into production environments, ensuring that unauthorized or untested changes are blocked.
Data Protection And Privacy Policy
Requires applications to implement privacy-by-design and ensure lawful handling, encryption, and retention of personal and sensitive data across all environments.
Secure Development Policy
Provides the broader framework for embedding security into the SDLC, of which this policy defines the concrete requirements and technical controls to be implemented within the application layer.
Incident Response Policy
Mandates structured handling of application security incidents, including vulnerabilities identified post-deployment or during pen testing, and outlines escalation, containment, and recovery procedures.
About Clarysec Policies - Application Security Requirements Policy
Effective security governance requires more than just words; it demands clarity, accountability, and a structure that scales with your organization. Generic templates often fail, creating ambiguity with long paragraphs and undefined roles. This policy is engineered to be the operational backbone of your security program. We assign responsibilities to the specific roles found in a modern enterprise, including the CISO, IT Security, and relevant committees, ensuring clear accountability. Every requirement is a uniquely numbered clause (e.g., 5.1.1, 5.1.2). This atomic structure makes the policy easy to implement, audit against specific controls, and safely customize without affecting document integrity, transforming it from a static document into a dynamic, actionable framework.
Built-In Exception Management
Formal exception request workflows with compensating controls, risk analysis, and mandatory risk register tracking.
Technical Control Detail
Outlines precise requirements for authentication, input validation, logging, and encryption tailored to each application type.
Mandatory Code & Security Testing
Requires SAST, DAST, SCA, penetration tests, and audit trails for every critical or externally exposed application.
Frequently Asked Questions
Built for Leaders, By Leaders
This policy was authored by a security leader with 25+ years of experience deploying and auditing ISMS frameworks for global enterprises. It's designed not just to be a document, but a defensible framework that stands up to auditor scrutiny.
